Rock cycle revision
Rock cycle revision game
Rock cycle MCQ's
Test your knowledge - rock cycle
Test your skills rock cycle
Diamonds
Rocks
Compounds and chemical equations revision
Compounds activity
ELEMENTS AND COMPOUNDS
Elements are simple substances which cannot be split up in chemical reactions.
Atoms are the smallest particles of an element that can exist. Atoms of an element
are all the same.
Each element has its own chemical symbol. For example, the chemical symbol for
oxygen is O.
Some elements have their atoms joined to each other in small groups called
molecules. Oxygen is an example.
Compounds
Elements can join together to make compounds. A compound contains two or more
elements joined together. The name of the compound tells you the elements that are
in it. Compounds made from two elements always have a name which ends in ‘-ide’.
Many compounds exist as atoms attached to each other in small groups – molecules.
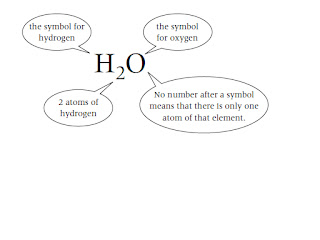
The chemical formula tells you the numbers of atoms of each element in a
compound. Each element in the chemical formula is shown by its chemical symbol.
For example:
A compound always contains the same elements in the same ratio.
The properties of a compound are different from the elements that make it up. For
example, hydrogen is an explosive gas and oxygen will relight a glowing splint but
water is a liquid which will put fires out.
Chemical reactions
Compounds can react chemically by mixing them with other chemicals, or by using
heat or electricity. You can tell that a chemical reaction has occurred if there is a
colour change or when a gas is given off.
Most chemical reactions also involve an energy change. This is usually in the form of
heat, but can also involve light being given off, for example, in burning (combustion).
In a chemical reaction a new substance is always formed. Most chemical reactions are
not easily reversed (they are irreversible).
Some chemical reactions take place just by mixing. When you make a solid by mixing
two liquids, the solid is called a precipitate.
Other chemical reactions need energy to start them off. This energy can be in the
form of heat, light or electricity. When you use energy to split up compounds they are
decomposed.
We can write word equations to show a chemical reaction. The chemicals that you
start with are called the reactants. The chemicals at the end are called the products.
For example:
Mixtures
Elements and compounds can also be mixed together. A mixture is easier to separate
than the elements in a compound. Soil, river water and sea water are examples of
mixtures that occur naturally.
Elements and compounds melt and boil at a fixed temperature. Mixtures do not have
definite melting points and boiling points.
Air is a mixture of gases – most of the air is nitrogen and oxygen. The gases in the air
can be separated by fractional distillation.
Elements, compounds and mixtures video
Minerals